Anúncios

Big Techs thrived during the global economic crisis of 2020, with the top five companies increasing their market value by over $1 trillion. But how did they achieve this?
What Are Big Tech Companies, and Why Are They Crucial?
When we talk about Big Tech, we’re referring to the tech giants that shape the digital world as we know it. Companies like Google, Amazon, Meta, Apple, and Microsoft are embedded in nearly every aspect of our daily lives—from the smartphone in your pocket and the e-commerce platforms you shop on, to the algorithms that curate your news feed.
These companies aren’t just big—they’re pillars of the global economy for several reasons:
- They concentrate a significant portion of capital and innovation within the tech sector.
- They influence everything from local economies to global trends.
- They create products and services that shape our behavior, such as search engine algorithms and social media platforms.
However, despite all this power, economic crises act as a stress test for these giants. In such times, Big Tech companies must prove their ability to reinvent themselves.
How Economic Crises Impact Big Tech
Economic crises have the ability to disrupt even the strongest tech giants. Despite their dominance, Big Tech companies are not immune to global turbulence. Let’s break down the ways these crises make their impact felt:
1. Decline in Consumer Spending and Advertising Revenue
In times of crisis, the logic is simple: people tighten their belts and cut spending on non-essential items. For companies like Apple, which rely heavily on device sales, this translates directly into lower demand. Meanwhile, platforms like Google and Meta, which depend heavily on advertising revenue, face a different challenge: advertisers spend less. In uncertain times, businesses tend to invest in cheaper, more immediate-return channels.
2. Operational Cost Challenges
Running a massive global operation is expensive—and during an economic downturn, every penny spent comes under scrutiny. Big Tech companies must grapple with enormous expenses, including teams of thousands of employees, energy-intensive data centers running 24/7, complex logistics, and hefty investments in research and development. In times of crisis, these areas inevitably undergo adjustments to ensure the company’s sustainability.
3. Regulation and Government Pressure
During economic crises, governments often step up their efforts to protect local markets and consumers. This frequently leads to stricter oversight of Big Tech companies. Issues like anticompetitive practices, data privacy, and taxation come under heightened scrutiny, forcing these giants to navigate a tighter regulatory landscape.
An example of this is the growing scrutiny directed at Meta and other tech giants in debates over free speech and global political influence. As analyzed in an article by The Verge, decisions such as the reinstatement of accounts belonging to controversial figures highlight how these companies face not only local regulations but also public pressure and geopolitical challenges. This illustrates the complexity of operating in an environment where Big Tech’s power is constantly being challenged by governments and society alike.
To learn more about how Big Tech navigates the challenges of regulation, public pressure, and global influence, read the full article on The Verge:
Strategic Repositioning: How Big Tech Adapts
If there’s one thing that defines Big Tech, it’s the ability to reinvent itself. During economic crises, these giants not only survive but also find innovative ways to reposition themselves, ensuring their relevance and competitiveness in the market.
Below is a summary table highlighting the main strategies these companies use to face challenges and create opportunities during uncertain times:
| Revenue Diversification | Expanding revenue streams to reduce risks during periods of instability. | Amazon invested in AWS (Amazon Web Services), which has become one of the company’s primary revenue sources. |
| Focus on Innovation and R&D | Betting on new products and technologies to lead the market during economic recovery. | After the 2008 crisis, Google launched Android, solidifying its presence in the mobile device market. |
| Expansion into Emerging Markets | Exploring regions with significant growth potential, such as Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Africa. | Meta invested in digital infrastructure in Africa to attract new users to its platforms. |
Impacts of Big Tech Repositioning on the Market
1. Supply Chain Ripple Effects
Global giants like Apple and Amazon have extensive supplier networks, and any adjustments to their supply chains can trigger a domino effect. During economic crises, the need to cut costs or restructure operations often leads to renegotiations or cancellations of contracts, creating challenges for smaller suppliers that rely on these agreements.
2. Labor Market Disruptions
Big Tech companies employ hundreds of thousands of people worldwide, and changes in their strategies have a direct impact on the job market. Massive layoffs, such as those recently implemented by Amazon and Meta, create waves of uncertainty. However, restructuring can also lead to new opportunities, particularly in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and technological sustainability.
3. Recent Evolution of Big Tech Market Value
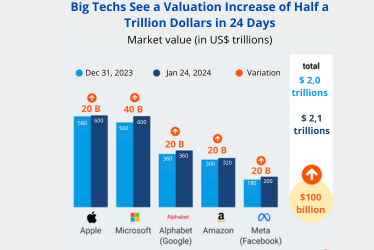
Big Tech entered 2024 with impressive momentum, once again demonstrating their resilience in a highly volatile market. In just the first 24 days of January, these giants saw a staggering $489 billion increase in their combined market value, reaching a total of $10.513 trillion on January 24.
This growth reflects these companies’ ability to reinvent themselves and seize new opportunities, even amidst global economic uncertainty. The surge in valuation was driven by factors such as expansion into emerging markets, the launch of new products, and the strengthening of essential services like cloud computing and artificial intelligence.
Examples of Big Techs in Action During Crises
How do these tech giants not only survive but thrive amidst economic crises?
Big Tech companies have demonstrated an exceptional ability to adapt during challenging times, employing strategies that not only ensure survival but often position them as leaders. Here are two examples of how they transform challenges into opportunities:
Microsoft
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a global economic crisis, but it also accelerated the shift to remote work. Microsoft capitalized on this scenario by heavily investing in indispensable tools such as Microsoft Teams and Azure, its cloud computing platform.
These services became vital for businesses and schools adapting to a new reality. As a result, Microsoft not only retained its relevance but also achieved significant growth during a period when many companies struggled to stay afloat.
Learn more about Microsoft’s role in enabling remote work during the pandemic:
Apple
Apple has a unique approach to navigating crises: it rarely lowers prices. Instead, it relies on customer loyalty and the perceived value of its products. Even during times of economic uncertainty, the company maintains stable profit margins, showcasing the strength of its long-term, premium positioning strategy.
This commitment to its “premium” identity has allowed Apple to weather crises without compromising its brand or profitability. While competitors may resort to discounts to attract customers, Apple reinforces its value as a symbol of quality and innovation.
Lessons from Big Tech During Crises
The examples above provide valuable insights on how to navigate tough times. Here are some key takeaways from Big Tech strategies:
1. Diversification Is Essential:
Relying on a single revenue stream is risky. Big Tech companies show that exploring diverse markets and products builds resilience. For instance, Amazon not only dominates e-commerce but also excels in cloud computing through AWS.
2. Innovation Is an Investment, Not a Cost:
During crises, innovation should be viewed as an investment, not a cost. Companies like Google and Microsoft continued funding R&D during downturns, resulting in game-changing products like Android and Microsoft Teams.
3. Adapt to Market Changes:
Success depends on staying attuned to market changes. Big Techs excel by pivoting quickly—whether by focusing on emerging markets, like Apple expanding into China, or optimizing supply chains to meet new demands.
The Future of Big Tech in a World of Uncertainty
In a world that’s becoming increasingly digital, Big Techs are not just surviving economic crises—they’re defining them. Their ability to adapt, innovate, and reposition themselves during challenging times sets the tone for the future of the global economy and technology. The next great transformation is just around the corner. Are we ready for it?
How do you think Big Techs will shape the economy in the coming decades?
References
HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW. The rise of big tech and antitrust implications.
MIT SLOAN MANAGEMENT REVIEW. Artificial intelligence and economic shifts in big tech.
BROOKINGS INSTITUTION. Brookings Institution.
STANFORD LAW REVIEW. Big tech regulation: global trends and local implications.